classification(3) -- VGG、Resnet、GoogLeNet、SPP-net
paper: VERY DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS FOR LARGE-SCALE IMAGE RECOGNITION
the winner and runner-up of localization and classification task in ILSVRC-2014.
Contributions
- increase depth of the network using an architecture with very small (3×3) convolution filters.
Architecture
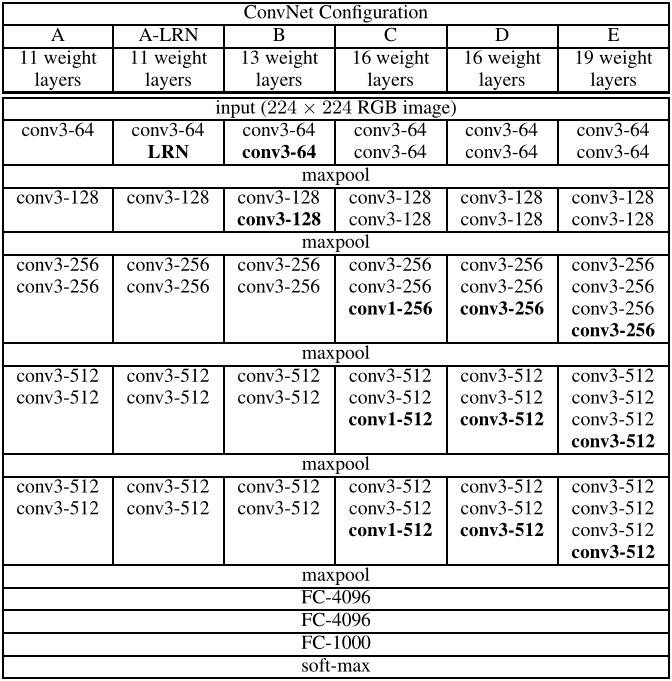
- use 1x1 conv in NIN to add depth.
- five max-poolinglayers are performed over a 2×2 pixel window, with stride 2.
- padding is 1 pixel for 3x3 conv.
- no LRN.
- pretrained VGG16 is the most frequently used.
- It is easy to see that a stack of two 3×3 conv layers has an effective receptive field of 5×5; three such layers have a 7×7 effective receptive field, but have fewer paramenters.
Training Details
- SGD optmizer, The batch size was set to 256, momentum to 0.9. The training was regularised by weight decay (the L2 penalty multiplier set to 5e−4 ) and dropout regularisation for the first two fully-connected layers. The learning rate was initially set to 1e−2 , and then decreased by a factor of 10 when the validation set accuracy stopped improving.
- randomly cropped from rescaled training images (one crop per image per SGD iteration).
- To further augment the training set, the crops underwent random horizontal flipping and random RGB colour shift.
pre-initialisation of certain layers, but found it can initialized by Glorot & Bengio

testing similar to OverFeat
- a speedup of 3.75 times on an off-the-self 4-GPU systerm.
Conclusions from Experiments
- LRN is useless.
- depth is important.
- in the same depth, 3x3 conv is better than 1x1 conv.
- The error rate of VGG saturates when the depth reaches 19 layers, it might need more data for training.
- scale jittering at both training and testing time leads to better results than fixed smallest side.
- dense convnet evaluation similar used in OverFeat is slightly worse than mult-crop evaluation used in GoogLeNet, but it’s high-efficiency.
- use ensemble method.
Localization
- a single object bounding box should be predicted for each of the top-5 classes.
- A bounding box is represented by a 4-D vector storing its center coordinates, width, and height. Training detail can refer to OverFeat.
- pretrained vggs is very good feature extractors.
paper: Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
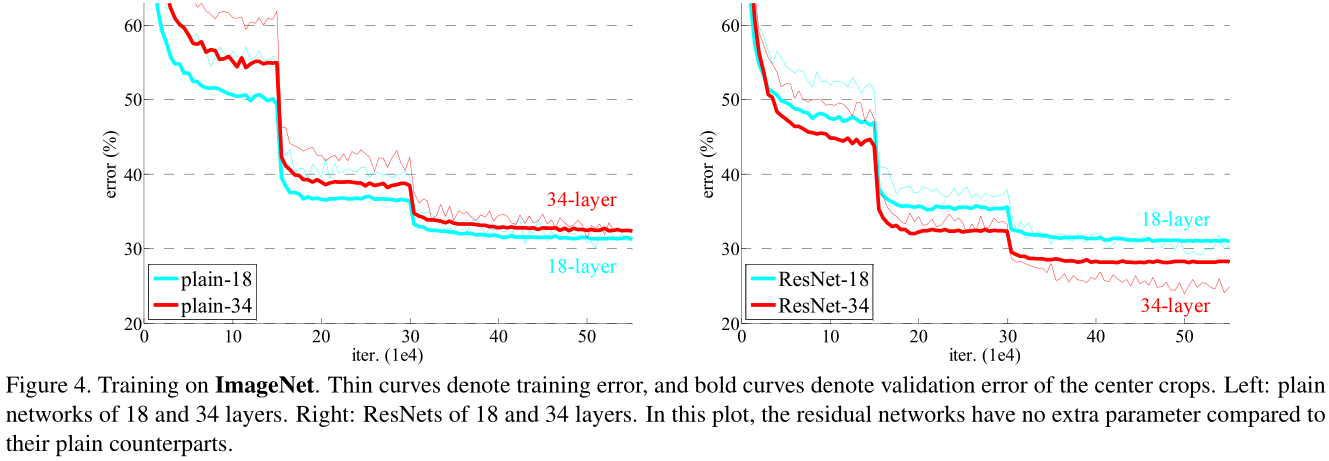
degradation problem
what is the problem ?
with the network depth increasing, accuracy gets saturated (which might be unsurprising) and then degrades rapidly, just as shown below. such degradation is not caused by overfitting.
Architectures
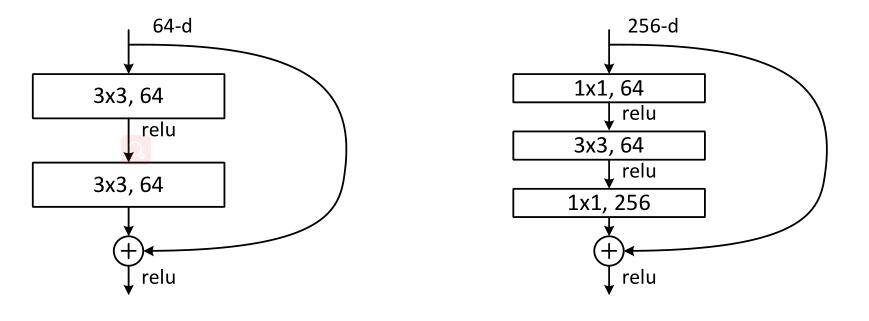
Above are residual blocks, left is used for shallow networks, right is used for deeper networks.


- plain version is similar to VGG, but performs downsampling directly by convolutional layers that have a stride of 2 and ends with a global average pooling and softmax.
- batch normalization is used after conv. ReLU activation function is used.
- residual block can solve the degradation problem, and can make model deeper.
paper: Going deeper with convolutions
The most straightforward way of improving the performance of deep neural networks is by increasing both their depth and width. But it makes a larger number of parameters which makes the enlarged network more prone to overfitting and increases use of computational resources. The fundamental way of solving both issues would be by ultimately moving from fully connected to sparsely connected architectures. But todays computing infrastructures are very inefficient when it comes to numerical calculation on non-uniform sparse data structures. how about an architecture that makes use of the extra sparsity, even at filter level, as suggested by GoogLeNet. It’s the winner of ILSVRC-2014 classification task.
Keys
- Inception module with dimension reduction
- Auxiliary classifiers
Inception module
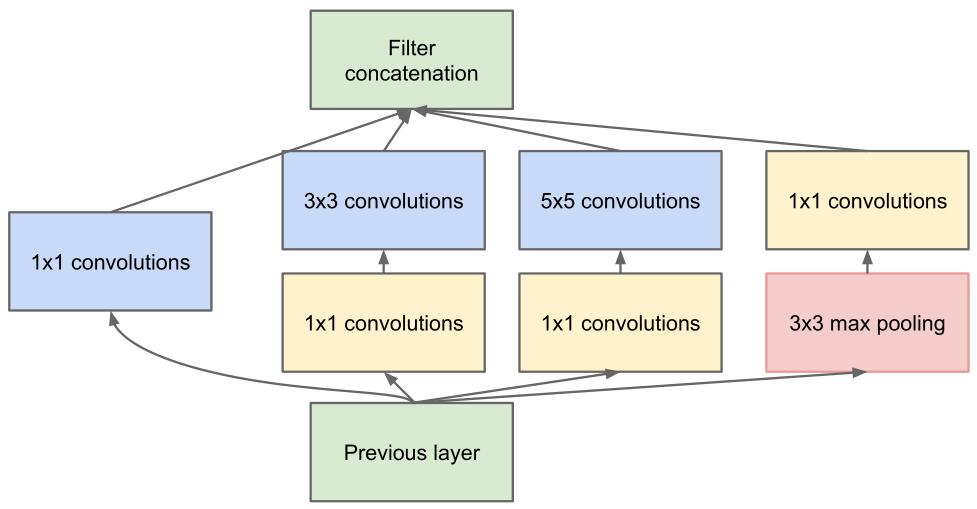
purpose of 1x1 conv in NIN:
- increase the representational power of neural networks
- dimension reduction
visual information should be processed at various scales (1x1, 3x3, 5x5 conv) and then aggregated so that the next stage can abstract features from different scales simultaneously.
GoogLeNet
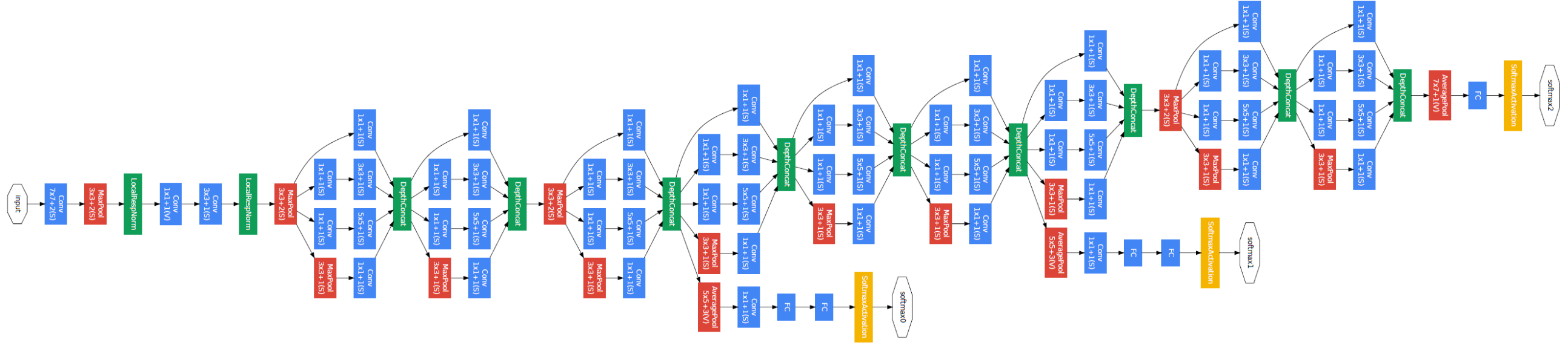
The network is 22 layers deep when counting only layers with parameters. The use of average pooling before the classifier which improves the performence is based on NIN. Auxiliary classifiers put on top of the output of the Inception (4a) and (4d) modules. During training, their loss gets added to the total loss of the network with a discount weight to 0.3. At inference time, these auxiliary networks are discarded. The other details are in the paper.
Training and Testing
no special training details but a set of techniques during testing to obtain a higher performance are as follows:
- ensemble prediction using 7 models.
- a more aggressive cropping approach than AlexNet. a) resize the image to 4 scales where the shorter dimension is 256, 288, 320 and 352 respectively; b) take the left, center and right square of these resized images (in the case of portrait images, we take the top, center and bottom squares); c) For each square, we then take the 4 corners and the center 224×224 crop as well as the square resized to 224×224, and their mirrored versions. This results in 4×3×6×2 = 144 crops per image.
- The softmax probabilities are averaged over multiple crops and over all the individual classifiers to obtain the final prediction.
Detection
- Similar to R-CNN, but is augmented with the Inception model as the region classifier.
- combining the Selective Search approach with multi-box predictions for higher object bounding box recall.
- In order to cut down the number of false positives, the superpixel size was increased by 2×.
- do not use bounding box regression due to lack of time.
paper: Spatial Group-wise Enhance: Improving Semantic Feature Learning in Convolutional Networks
Because of fc layers, CNNs require a fixed input size. We can solve it by replacing fc layers with convolutional layers and then averaging which is used in OverFeat. Or using SPP layer in this paper.
How SPP layer work
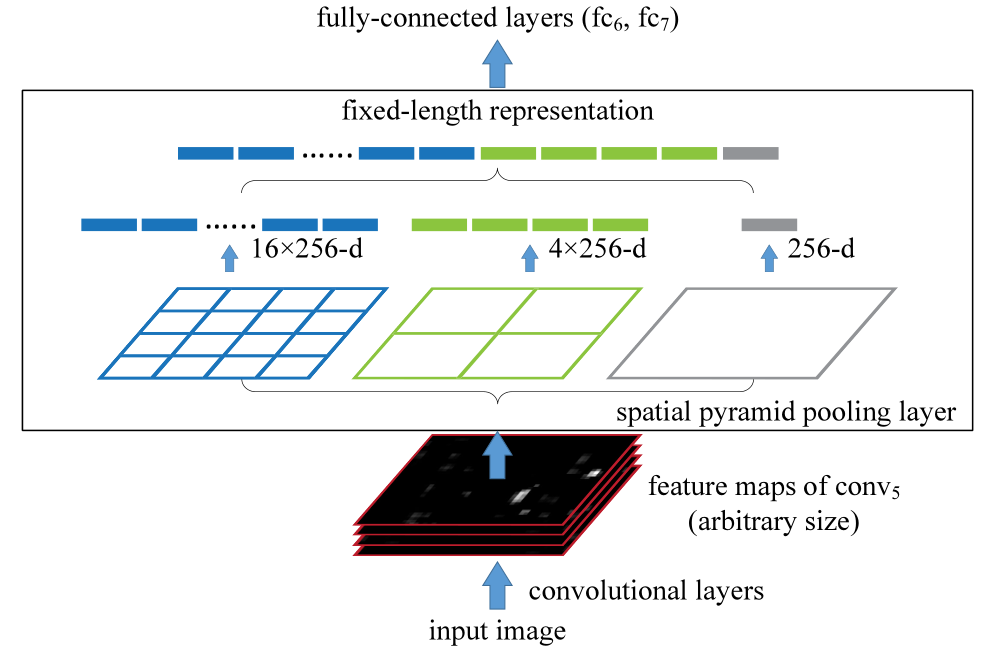
It uses multi-level spatial bins to get fixed-lenght vectors, and then feed the fixed vector to fc layer.
SPP layer can be used for classic CNN models by replaceing the last pooling layer with SPP layer as baseline.
SPP-net for Detection
R-CNN costs much time for feature extraction, because CNN extracts features for each region proposal of 2k~ obtained by selective search.
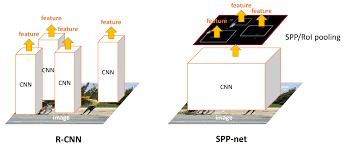
SPP-net-based system computes features 24-102× faster than R-CNN. It can run the convolutional layers only once on the entire image (regardless of the number of windows), and then extract features by SPP-net on the feature maps.